Which Technology Should AVOD Players Leverage: SSAI or CSAI?
AVOD is here to stay!
With the subscriber churn hitting an unprecedented high, it is quite evident that the ad-based model is what the OTT giants are inclining towards.
Of course, the subscription ecosystem is not dying anytime soon. However, there is a spike in platforms beginning to capitalize on ads now more than ever.
In fact, stats reveal that VOD platform video advertising is the largest segment holding a whopping market volume of $183 billion.
But, to reign supreme in the AVOD landscape, content owners ought to first decide upon the technology that should be instilled to deliver ads to the end-user.
Recommended Read: How AVOD is driving the OTT game?
Table of Contents
What is OTT Ad Insertion?
Ad agencies are aplenty and want to make use of every possible medium to take their brand to the next level. Publishers on the other hand, have begun leveraging this trend to garner the best monetary results.
However, the ad landscape has radically changed over the past few years. It is targeted advertising, brands are keen on and similarly, online video platform too are extremely cautious about delivering ads that are personalized, and not cause annoyance.
Hence arose the concept of DAI (Dynamic Ad Insertion), a server-side ad technology that ensures personalized ads are delivered to the intended audience by making use of insights from geolocalization, socio-demographics, and behavioral profiles per device, content, and user.
An Overview of SSAI (Server-Side Ad Insertion)
Otherwise called ad stitching, SSAI integrates ads into the streams, unlike CSAI, where the client (media player) places ads in a pre-defined fashion.
But, when it comes to SSAI, the server stitches the ads directly into the video content, delivering a seamless viewer experience. This gives audiences a feeling of watching a continuous stream rather than intrusive ad breaks.
Moreover, it solves a serious issue that exists with CSAI. Since the ads are stitched together with the streams and it appears as a continuous sequence of video data, ad blockers don’t work with SSAI and the ads are played anyway.
Talking about CSAI (Client-Side Ad Insertion)
When it comes to CSAI, the client (video player) sends a request to the ad server and gets the ad delivered based on the ad marker placed in the video content. Once the player receives the ad, the existing stream is paused for an ad break and resumes playing once the commercial is completed.
Recommended Reading
CSAI ads can be placed in a pre-roll (before the start of a video), mid-roll (in the middle of a video), or in a post-roll (after the video completes) fashion.
How does CSAI & SSAI Differ Technically?
In the CSAI workflow, the video stream delivered to the viewer via a CDN (Content Delivery Network) is stopped when an ad marker is reached.
Next, the video player makes a call to the ad server, requesting for the ad and in turn, receives a VAST XML with all the relevant information concerning the ad.
Now, the video commercial is played, following which the player switches back to the original video content and continues streaming.
Later, the ad-related data such as completion rates, etc is collected and taken to the ad server for report generation on ad performance.
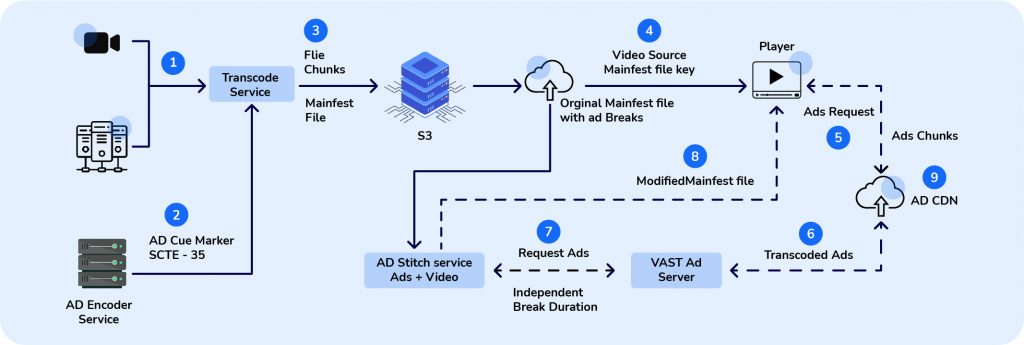
In the SSAI workflow, when the viewer reaches an ad break, unlike the client directly sending a request to the ad server, the SSAI server calls for an ad from a 3rd party ad-decision server in real time.
The request sent contains viewer data required for picking a personalized ad.
The 3rd party ad server now responds with an ad to the SSAI module.
The targeted ad chunks are then stitched into the content stream which is then pushed to the CDN from where the original video & ad are delivered as a continuous stream to the viewer.
Lastly, the tracking video streaming servers collect the ad-related data such as views and impressions for data-deiven decisions.
To summarize,
CSAI(Client Side Ad Insertion) |
SSAI(Server Side Ad Insertion) |
| Works based on the client (video player) initiating a request & the ad server responding with the ad | Also referred to as ad stitching, ads are directly embedded to the video stream at hand |
| Ads and the video content are independent of each other | Ensures smoother playback since the video with the ads are played as a single stream |
| Client has to constantly switch between the ad and the actual video, leading to latency issues | Eases the strain off the client |
| Ad-blocking extensions might hinder the commercial from playing | Can bypass ad blockers |
The Verdict,
The answer is quite subjective and depends on various factors such as the need to bypass ad blockers or deliver a rich ad experience.
Both SSAI and CSAI have their own pros and cons which should be weighed logically to determine which technology would most suit your ad-based platform.
For instance, server-side insertion offers seamless viewing, protects against ad blockers, and ensures reduced latency, but has its own downsides in issues concerning spoofing, and the complex infrastructure that goes behind the working.
Similarly, the client-side ad insertion ranks high on tracking and metrics and delivering rich ad experiences but is susceptible to ad blockers, which can cause monetary losses on the publisher.
Hence, it is essential to make wise decisions keeping in mind the overall budget, low-latency requirements, and user experience to ultimately deliver ads you can garner profits from.