Start and Grow Your Online Video Streaming Platform With 1000+ Features & 10+ Revenue Models.
Book a Free DemoWhat Is Video Streaming? Meaning, Definition & How It Works?

Summarize this article via
Previously, video consumption was rigid; content had to be downloaded, broadcast at fixed times, or accessed through physical media. Fast forward a few decades, and video streaming has completely transformed how content is delivered and consumed. Today, streaming enables instant, on-demand playback across devices, powered by the internet and sophisticated delivery technologies that bring video to audiences anywhere, at any time.
This shift is not limited just to video consumers. In fact, 91% of businesses use video as a marketing tool, as internet video delivery remains the popular distribution channel for such entities. As a result, video streaming platforms are increasingly central to how organizations manage, deliver, and scale video content.
This blog explores what video streaming is, how video streaming works, and why it outpaces traditional downloading in terms of speed, flexibility, and convenience.
Table of Contents
What is Video Streaming?
Video Streaming is a real-time transmission of compressed video files over the internet, where the video player of an online video streaming platform reassembles them to provide smooth viewing, courtesy of HTTP-based protocols (HLS, DASH). Online video streaming acts as a central hub, facilitating encoding, decoding, and video exchange across mobile phones, smart TVs, and desktops.
How does Video Streaming Work?
Video streaming begins when a viewer requests to access the video. Upon receiving the request, the server compresses the pre-recorded video files into small chunks and sends them to the requesting device. Upon receiving the video files in small chunks, the video player on the requesting device will decompress the data to show immediate playback.
Video delivery, traditionally, mandated users to download video files for full playback. However, with the advent of cloud video streaming, video files can be accessed from cloud ‘remote’ servers anywhere, anytime.
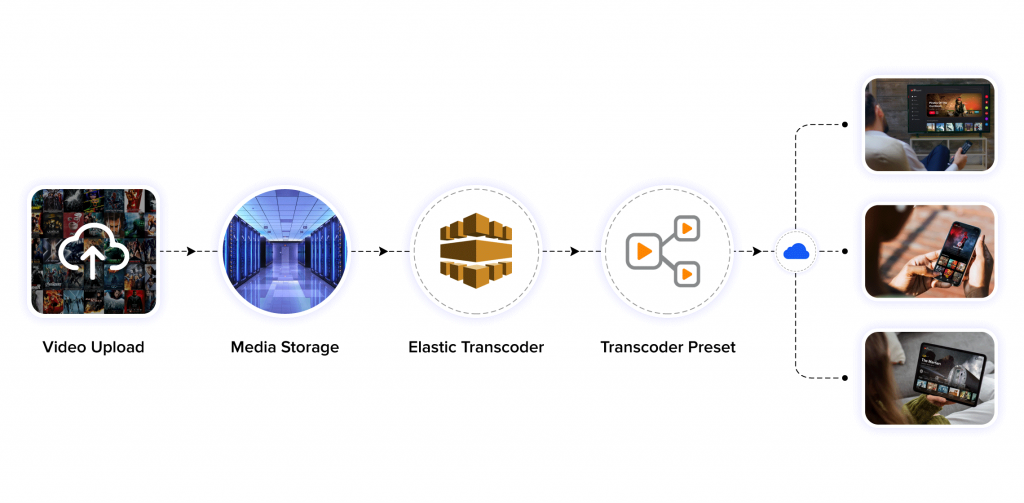
Modern video streaming relies on streaming protocols (like HLS) that manage video delivery, buffering, and adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) based on network conditions. These protocols enable smooth playback by dynamically adjusting video quality based on available bandwidth, ensuring minimal buffering across devices and network environments.
Streaming vs Downloading: What’s the Difference?
Downloading allows playback only when the complete copy is saved locally, whereas streaming facilitates immediate playback upon requesting access to the video. When a video file is downloaded, it consumes a specific storage space on your device. Streaming, in hindsight, eliminates waiting times and avoids filling up device storage as only small chunks of data are transferred at once.
When files are saved locally as media files (e.g., MP4, MKV), enforcing digital rights protection becomes impossible. However, streaming platforms gain more control over their content, as they can enforce digital rights management (DRM) solutions and prevent unauthorized copying, unlike downloading.
Downloading allows the video to be viewed in a static quality, whereas real-time streaming leverages adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) to adjust video quality based on dwindling network conditions. For this reason, content owners, broadcasters, and media enterprises have embraced streaming to distribute their video content.
Having said that, modern streaming platforms have incorporated the download option (not locally though!) that allows viewers to enjoy offline playback.
Benefits of Video Streaming
Video streaming delivers advantages not only to the organizations that distribute content, but also to the audiences that consume it. These benefits can be understood from two perspectives: businesses and viewers.

For Businesses
* Enhanced Engagement: Video streaming enables organizations to deliver content in a more engaging and interactive format than text or static media. As a result, brand engagement video has become a key component of modern business video marketing strategies.
* Global Reach: Broadcasting companies can distribute their content across regions and time zones, thanks to a truly global video CDN. This scalability makes video streaming an effective channel for enterprises aiming to expand their digital presence and reach wider audiences.
* Audience Analytics: Businesses can track metrics such as watch time, engagement levels, drop-off points, and viewer demographics. These insights help refine digital video strategy, optimize content performance, and support data-driven decision-making across marketing and communications teams.
* Video Monetization Revenue: Video streaming opens up multiple revenue streams for content businesses. When someone tries to build a streaming app, they can monetize content through subscriptions, advertising, pay-per-view, or gated access.
For Viewers
* No Downloads Required: Video streaming enables viewers to watch content instantly, eliminating the need to download full video files beforehand. Playback begins as soon as a video is requested, eliminating long waiting times and the need to manage storage space on personal devices.
* Cross-Device Playback: Viewers can start white label video streaming on a smartphone, continue on a laptop, and finish on a smart TV. This cross-device compatibility ensures a consistent viewing experience regardless of screen size or platform.
* Adaptive Video Quality: When internet speeds fluctuate, the video player switches between quality levels to maintain smooth playback and reduce buffering. This ensures viewers receive the best possible viewing experience without manual adjustments.
Looking To Build Your Own Online Video Platform?
Start and Grow Your Video Streaming Service With 1000+ Features & 9+ Revenue Models.
Highly Customizable
Life Time Ownership
Own 100% of Your Revenue
Full-Branding Freedom
Key Features Involved in Video Streaming
To understand how video streaming functions at scale, it is important to first examine the core technical components that enable video delivery, playback, and performance.
Core Technical Components
1) Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR)
Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR) is a technological process for delivering video that dynamically adjusts quality in real-time based on the viewer’s internet speed and device. ABR begins by encoding a single video file into multiple versions (renditions) at different bitrates (e.g., 1080p, 720p, 480p). Then, the video player chooses the best-quality file that the device can play with the smallest amount of buffering (if not zero buffering).
2) Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A content delivery network or content distribution network (CDN) is a network of geographically distributed servers around the world. CDN works on a process called caching that temporarily stores copies of your video files in those distributed servers. When a viewer requests specific video content, the nearby server of a video CDN delivers a copy of that video file, thereby reducing buffering and resulting in a smooth playback.
3) Video Encoding & Transcoding
Encoding compresses the overall size of the video file without compromising the overall quality, whereas video transcoding involves optimizing videos to ensure seamless playback. Some popular video codecs used are H.264, VP9, and H.265 (HEVC). These codecs deliver sharp visuals without consuming excessive bandwidth or storage space.
4) Streaming Protocols
Streaming protocols are a set of rules or standards that determine the transmission of video data from one device to another, over the Internet. These protocols are essential for ensuring smooth, reliable video playback across various devices and networks. Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP), HTTP Live Streaming (HLS), MPEG-DASH, and Web Real-Time Communications (WebRTC) are some of the common streaming protocols.
User Experience (UX) Features
1) Multi-Device Compatibility
Multi-device compatibility also allows users to switch between devices without interrupting their viewing experience. This ensures viewers can access the same content seamlessly, regardless of screen size or operating system.
2) Offline Viewing/Downloads
Offline viewing enables users to watch video content without an active internet connection. Instead of saving video files locally, streaming platforms store encrypted video data within the application, allowing temporary access under controlled conditions.
3) Player Controls
Player controls allow viewers to manage video content, with controls like play, pause, volume adjustment, playback speed, captions, and quality selection. These controls give users flexibility over their viewing experience and ensure accessibility across different user needs and preferences.
Platform & Content Management Features
1) Content Management System (CMS)
A CMS, especially an enterprise video content management system, allows businesses and media teams to upload videos, manage metadata, categorize content, and control access from a central dashboard. The CMS simplifies content workflows and ensures videos are easy to discover and distribute.
2) Live Streaming & VOD
Video streaming works in both ways: live and video on demand (VOD) delivery. Live streaming enables real-time broadcasting of live events, whereas VOD allows viewers to watch pre-recorded content at their convenience.
3) Security & DRM
Security and digital rights management (DRM) protect video content from unauthorized access, copying, and redistribution. Streaming platforms use encryption, access controls, and DRM technologies to enforce content usage rules. These measures help content owners maintain control over their intellectual property while delivering video securely.
4) Real-time Analytics
Real-time analytics provide immediate insights into how viewers interact with video content. Metrics such as concurrent viewers, watch time, engagement levels, and drop-off points help businesses monitor performance. These insights support faster decision-making and content optimization.
Monetization & Business Features
1) Flexible Monetization Options
Monetization options allow businesses and media-tech enterprises to generate revenue from their video content. While subscriptions (SVOD) enable video monetization with recurring revenue, advertisements (AVOD) unlock revenue from ad inventories (despite offering free content access to viewers). Pay per view streaming (TVOD) unlocks revenue for each transaction.
2) Geo-blocking
Geo-blocking enables content owners to restrict video access based on geographic locations. From both business and monetization standpoints, this helps massively, as content licensing agreements mandate geographic restrictions, thereby maximizing revenue from intended markets.
Advanced & Future Technologies
1) AI-Powered Enhancements
AI capabilities in video streaming are plenty. Through machine learning video analytics, platforms can analyze viewer behavior, detect engagement patterns, and optimize playback quality. The automated content moderation helps content owners identify inappropriate or restricted content at scale. Plus, you may know, AI recommendations dominate video streaming platforms with their relevant content suggestions.
2) VR/AR Integration
VR and AR integration support 360-degree video streaming, allowing viewers to explore environments rather than passively watch content. These technologies are commonly used in entertainment, training, virtual events, and simulations, offering more interactive and engaging viewing experiences.
3) Ultra-Low Latency
Ultra-low latency streaming focuses on reducing the delay between video capture and playback to near real-time levels. This is especially important for live sports, gaming, auctions, and interactive broadcasts where timing is critical. By minimizing latency, streaming platforms can deliver more responsive and synchronized viewing experiences for live audiences.
Limitations and Challenges of Video Streaming
While video streaming offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain technical and operational challenges that businesses must address to deliver consistent and reliable viewing experiences.
* Bandwidth & Latency: Limited bandwidth leads to buffering, reduced video quality, or playback interruptions, while high latency can cause noticeable delays, especially during live streams.
* Scalability: Scaling video delivery to support thousands or millions of concurrent viewers requires robust infrastructure, efficient content delivery networks (CDNs), and load management. Without proper scalability planning, platforms may experience outages or performance bottlenecks.
* Device Compatibility: Compatibility issues may arise due to differing hardware capabilities, software updates, or unsupported formats. Viewers access video content across a wide range of devices, operating systems, browsers, and screen sizes. Ensuring consistent playback and performance across all these environments can be challenging.
* Content Piracy: Unauthorized copying, redistribution, and recording of video content remain ongoing challenges in streaming. Even with protective measures in place, content can be illegally shared through screen recording or external capture methods. Piracy reduces revenue potential and undermines content ownership.
* Cyber Threats: Streaming platforms are exposed to various cyber threats, including account takeovers, credential abuse, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and malicious traffic. These threats can disrupt service availability and compromise user trust if not adequately addressed.
How To Create & Launch Your Own Video Streaming Platform
After understanding the fundamentals, benefits, and challenges of video streaming, the next step is to explore how a video streaming platform can be created and launched. Any business that wants to build a video streaming website should start with:
1) Plan Your Service
The first step in creating a video streaming platform is defining its purpose and audience. This includes identifying the type of content you plan to offer, the viewing experience you want to deliver, and the business goals behind the platform. Clear planning helps guide technical decisions and content strategies later in the process.
2) Choose Your Platform and Tech
Selecting the right technology stack is critical for reliable video delivery. This involves choosing video hosting infrastructure, streaming protocols, content delivery networks (CDNs), and player technology. Businesses must also decide whether to build from scratch or use existing video streaming frameworks, depending on technical expertise and time-to-market requirements.
3) Build & Populate Your Platform
Once the technical foundation is in place, the platform can be configured and populated with content. This includes uploading videos, organizing content libraries, setting metadata, and designing the user interface. Testing playback, performance, and device compatibility at this stage helps ensure a smooth viewing experience.
4) Secure & Monetize
Security measures such as encryption, access controls, and digital rights management (DRM) protect content from unauthorized use. At the same time, monetization models such as subscriptions, advertising, or pay per view can be implemented to generate revenue. Balancing protection with accessibility is key to maintaining user trust and business viability.
5) Launch & Grow
Launching a video streaming platform involves making the service available to users and monitoring initial performance. Post-launch, continuous optimization is important, including refining content offerings, improving user experience, and analyzing viewer data. Ongoing updates and engagement strategies support long-term growth and scalability.
Conclusion
Video streaming has become a foundational component of modern digital communication and content delivery. By enabling real-time and on-demand access to video across devices, streaming has reshaped how audiences consume content and how businesses distribute it at scale.
As explored throughout this blog, video streaming combines technical components such as adaptive bitrate delivery, content security, analytics, and monetization with emerging capabilities like AI-driven optimization and immersive media experiences. At the same time, it presents challenges related to infrastructure, security, and content rights that must be carefully managed.
- Request Demo Book a Live, Personalized Demo
- Contact Sales Reach Out to Our OTT Experts
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
1. Why Is Streaming video Important For Your Business?
Professional-grade video streaming provides a great value while investing since consumer-grade solution aren’t capable of satisfying needs of large businesses. When it comes to video streams, they are cloud-based and provide advanced features like cutting-edge tech-stack, 6+ monetization models, everlasting ownership, robust CMS, first-class security, etc.
2. What Are The Different Types Of Video Streaming?
As global trends have been influencing consumer viewing habits the definition of streaming video sets to expand across wide range of niches. The media content is in the form of live or recorded streams, which are delivered to web, mobile or varied connected devices. Some of the common forms of streaming content are webcasts, podcasts, movies, TV shows, etc.
3. What Are The Benefits Of Streaming Video?
Some of the benefits that streaming businesses can own comprise of downloadable content at any circumstance, rendition of videos at flexible resolutions, reduced cost due to increased accessibility of the streaming, data storage is not with physical servers but on cloud, enhanced customer experience due to flexible options in playback, etc.
4. How To Start A Video Streaming Business?
While you tend to own up streaming videos you can set your revenue model to rapidly increase streaming ROI. Also you can leverage on the facility of centralized storage, ensure flexible payment gateways, choose a standard embed player, get network of server connected to each other for smooth delivery of content, instill security paywalls, & much more.
5. How Do I Monetize Video Content?
You can now independently stream & monetize on demand as well as live streaming content with major monetization models like Subscription VOD, Advertising VOD, Transactional on demand, Premium VOD, Video Paywalls, Coupons & promotions & lots more.